What is the Mood Meter?
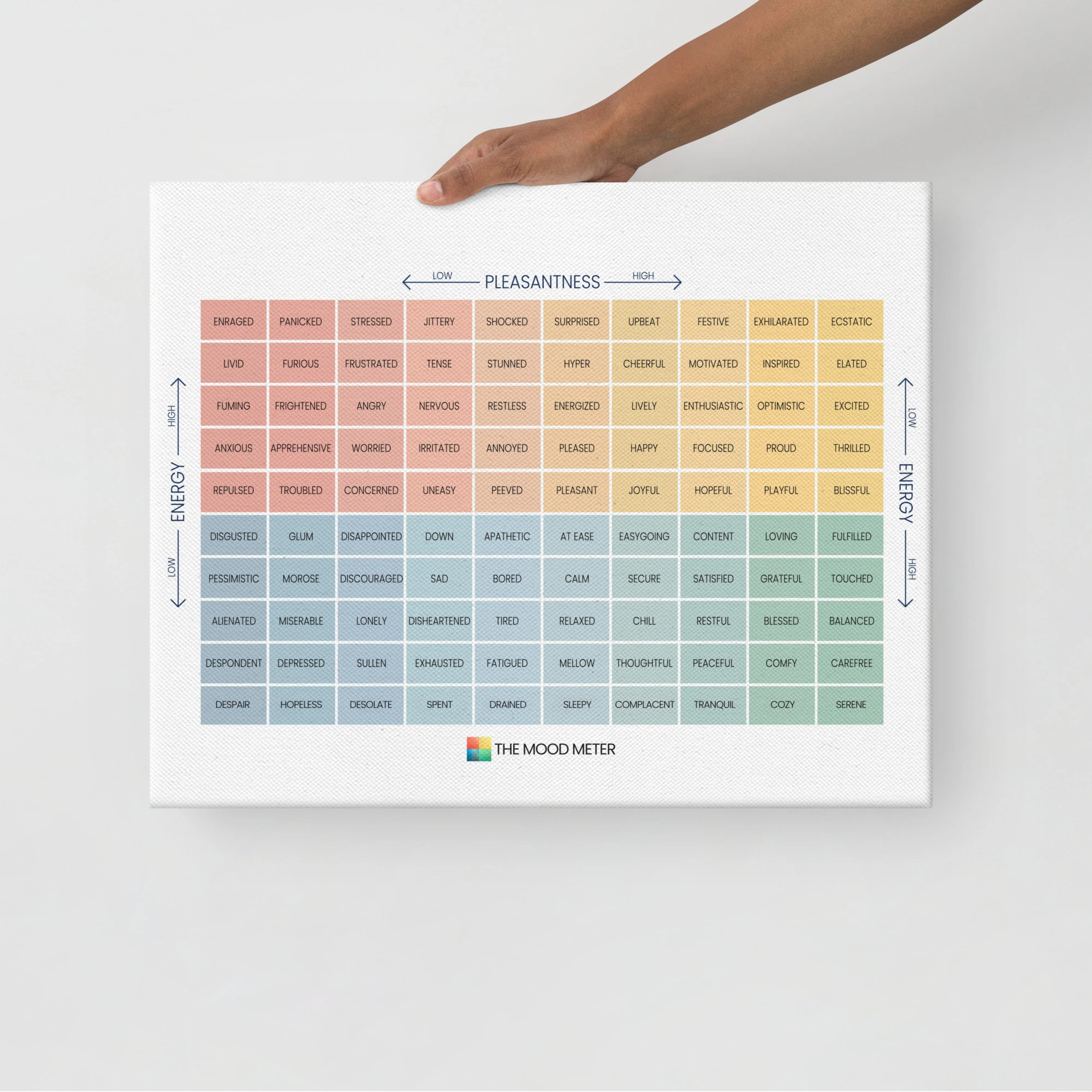
Understanding and managing emotions is a critical part of both personal well-being and effective learning. One tool that has gained international recognition for helping individuals recognize, label, and regulate their emotions is the Mood Meter. Developed by researchers at the Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, the Mood Meter is a simple yet powerful framework designed to help people cultivate emotional awareness and build emotional intelligence skills in daily life. Understand more about the Mood Meter.
The Origin of the Mood Meter
The Mood Meter was created as part of the RULER program, an evidence-based approach to social and emotional learning. Dr. Marc Brackett and his team at Yale developed this visual tool to provide students, educators, and professionals with a structured way of identifying how they feel at any given moment. By using the Mood Meter consistently, people begin to build emotional vocabulary, increase self-awareness, and develop strategies for managing their feelings more constructively. Learn more about the history and benefits of Mood Meter.
The Four Quadrants
The Mood Meter is divided into four quadrants, each representing different emotional states based on two axes: energy level (from low to high) and pleasantness (from unpleasant to pleasant).
-
Red Quadrant (High Energy, Unpleasant Feelings):
Emotions such as anger, frustration, anxiety, and stress fall into this category. While often considered negative, these emotions can also serve as signals that something important needs attention. Read more about Red Quadrant of the Mood Meter. -
Blue Quadrant (Low Energy, Unpleasant Feelings):
Feelings like sadness, disappointment, loneliness, and fatigue are placed here. These emotions highlight moments of loss, need for rest, or the importance of reflection. Read More about Blue Quadrant of the Mood Meter. -
Yellow Quadrant (High Energy, Pleasant Feelings):
Emotions such as excitement, joy, enthusiasm, and optimism are found in this quadrant. They often drive creativity, motivation, and social connection. To understand the yellow quadrant of the Mood Meter, read the complete article. -
Green Quadrant (Low Energy, Pleasant Feelings):
Calmness, contentment, relaxation, and peacefulness belong here. These states support focus, recovery, and mindful decision-making. Learn more about the green quadrant of Mood Meter in this guide.
By plotting emotions along these axes, individuals gain clarity on their emotional state and can respond in healthier, more intentional ways.
Why the Mood Meter Matters
The Mood Meter is not just a chart—it is a tool for lifelong learning and emotional growth. Its benefits include:
-
Self-Awareness: Naming emotions helps reduce confusion and gives people a sense of control.
-
Emotional Regulation: Once individuals know what they feel, they can apply strategies to shift their state if necessary.
-
Improved Relationships: Understanding one’s own emotions and those of others fosters empathy and more effective communication.
-
Better Decision-Making: Recognizing how emotions influence choices allows for more balanced and thoughtful actions.
Research suggests that people who consistently use tools like the Mood Meter tend to experience lower stress levels, improved focus, and stronger connections with others.
How the Mood Meter is Used
The Mood Meter is widely implemented in schools, workplaces, and personal development programs. Teachers may ask students to check in on the Mood Meter at the start of the day, encouraging them to express how they feel openly. Businesses also use it in leadership development and team-building exercises, promoting a culture where emotions are acknowledged and respected.
For individuals, using the Mood Meter might involve pausing during the day to reflect: Where am I on the chart? Do I want to stay here, or do I need to shift my state? This practice encourages mindfulness and intentional action.
Practical Steps to Apply the Mood Meter
-
Pause and Check-In: Take a moment to identify your current energy and pleasantness levels.
-
Name the Feeling: Expand your emotional vocabulary by choosing precise words (e.g., “irritated” instead of just “mad”).
-
Reflect on Causes: Ask yourself what triggered this emotion and what it might be teaching you.
-
Choose a Strategy: Decide whether to stay in that state or shift (through deep breathing, movement, or reframing thoughts).
The Mood Meter is more than a colorful diagram; it is a gateway to understanding the complexities of human emotions. By regularly engaging with it, individuals strengthen their emotional intelligence, enhance communication, and foster healthier relationships. In schools, homes, and workplaces alike, the Mood Meter serves as a reminder that emotions are not problems to be solved but information to be understood and used for growth. A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Enhancing Emotional Intelligence through Mood Meter.