The 5 Elements of Emotional Intelligence: A Complete Guide to Goleman’s EQ Model
Mastering Goleman’s Five Elements of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence (EQ) determines how effectively we understand ourselves, interact with others, and make sound decisions under pressure. Daniel Goleman’s framework identifies five core elements, self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, that shape how we navigate relationships, leadership, and personal effectiveness. We present a comprehensive, research-driven guide written in a formal “we” voice, designed to provide more depth, clarity, and practical insight than typical summaries of EQ.
Self-Awareness: Understanding Internal States With Precision
We begin with self-awareness because it serves as the foundation for all other EQ competencies. Self-awareness involves recognizing our emotions, understanding why they arise, and evaluating how they influence our actions. High self-awareness allows us to identify triggers, strengths, blind spots, and habitual responses.
We emphasize contextual reflection, journaling, real-time emotional labeling, and cognitive reframing as essential tools for strengthening this skill. Leaders with strong self-awareness demonstrate steadier decision-making, clearer communication, and better alignment between values and behavior.
Self-Regulation: Managing Emotions Constructively
Self-regulation is the ability to control impulsive reactions, stay adaptable, and sustain emotional balance during challenges. We frame self-regulation as a practice of choice rather than suppression, learning to interrupt automatic responses, manage conflict calmly, and apply deliberate problem-solving.
Advanced strategies include cognitive defusion, situational reframing, and breath-based nervous-system resets. When individuals regulate effectively, they create environments built on trust, predictability, and psychological safety. In leadership and teamwork, this competency directly elevates resilience, team morale, and performance.
Motivation: Driving Performance Through Purpose and Persistence
Goleman describes motivation as a deep, intrinsic drive that goes beyond external rewards. We define motivation within EQ as the commitment to goals, willingness to persevere, and ability to maintain optimism even during setbacks.
We highlight techniques such as structured goal systems, habit stacking, personal values alignment, and performance reflection frameworks. Motivated individuals consistently outperform expectations because their ambitions are fueled by purpose rather than pressure.
Empathy: Understanding Others’ Emotions and Perspectives
Empathy expands EQ beyond the self. It involves perceiving emotional cues, interpreting unspoken needs, and responding with clarity and compassion.
We distinguish three forms of empathy: cognitive (understanding someone’s thoughts), emotional (feeling with them), and compassionate (taking helpful action).
High-empathy professionals build stronger relationships, resolve conflicts quickly, and foster inclusive environments. Empathy also improves negotiation outcomes, customer relationships, and cross-cultural communication.
Social Skills: Building Meaningful, High-Functioning Relationships
Social skills represent the outward expression of emotional intelligence, how individuals influence, collaborate, and lead.
This includes communication clarity, conflict resolution, persuasion, rapport-building, and team leadership. We outline advanced techniques such as active inquiry, reflective listening, strategic storytelling, and emotional signaling awareness.
Individuals with strong social skills navigate complex interpersonal dynamics with ease and become catalysts for productivity and cohesion.
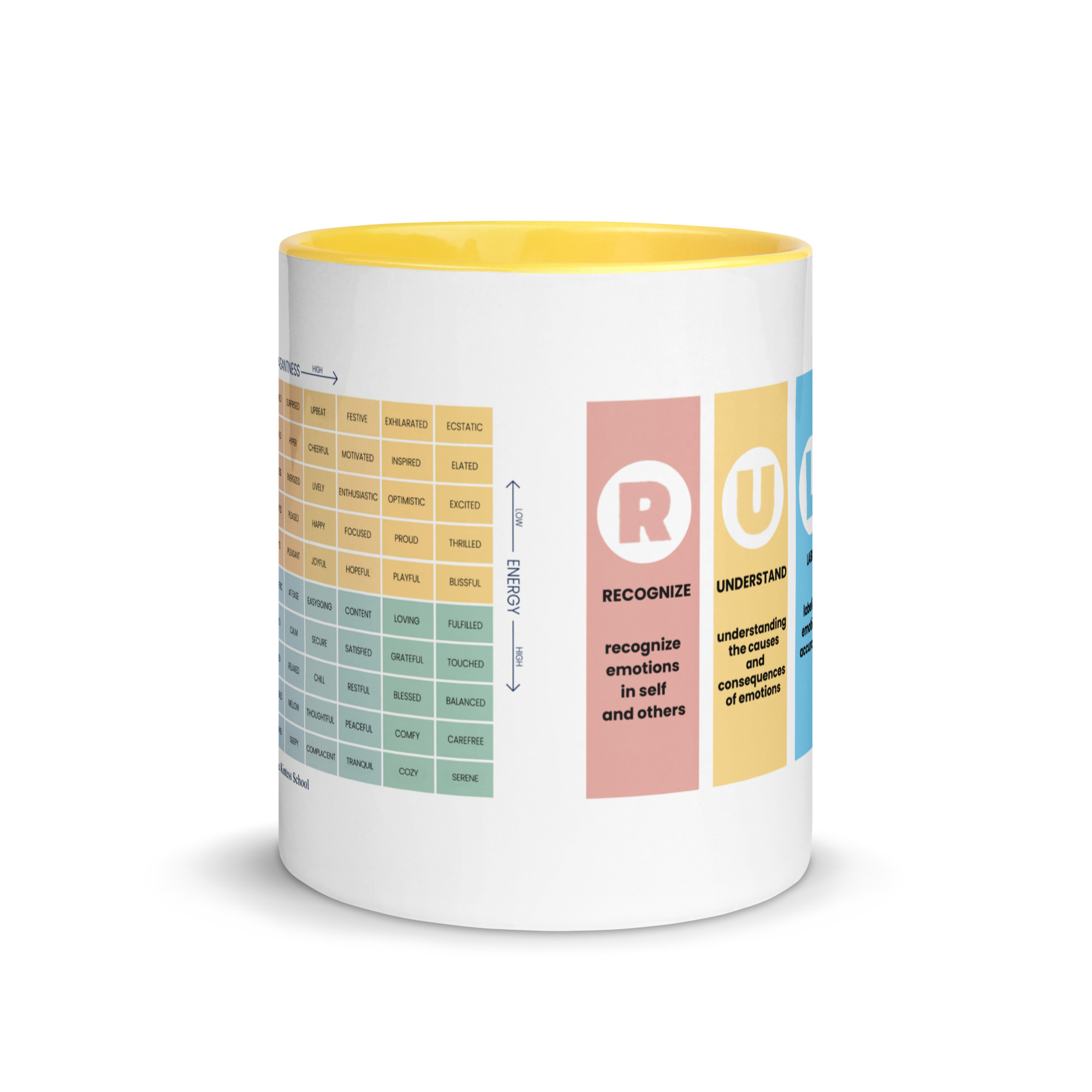
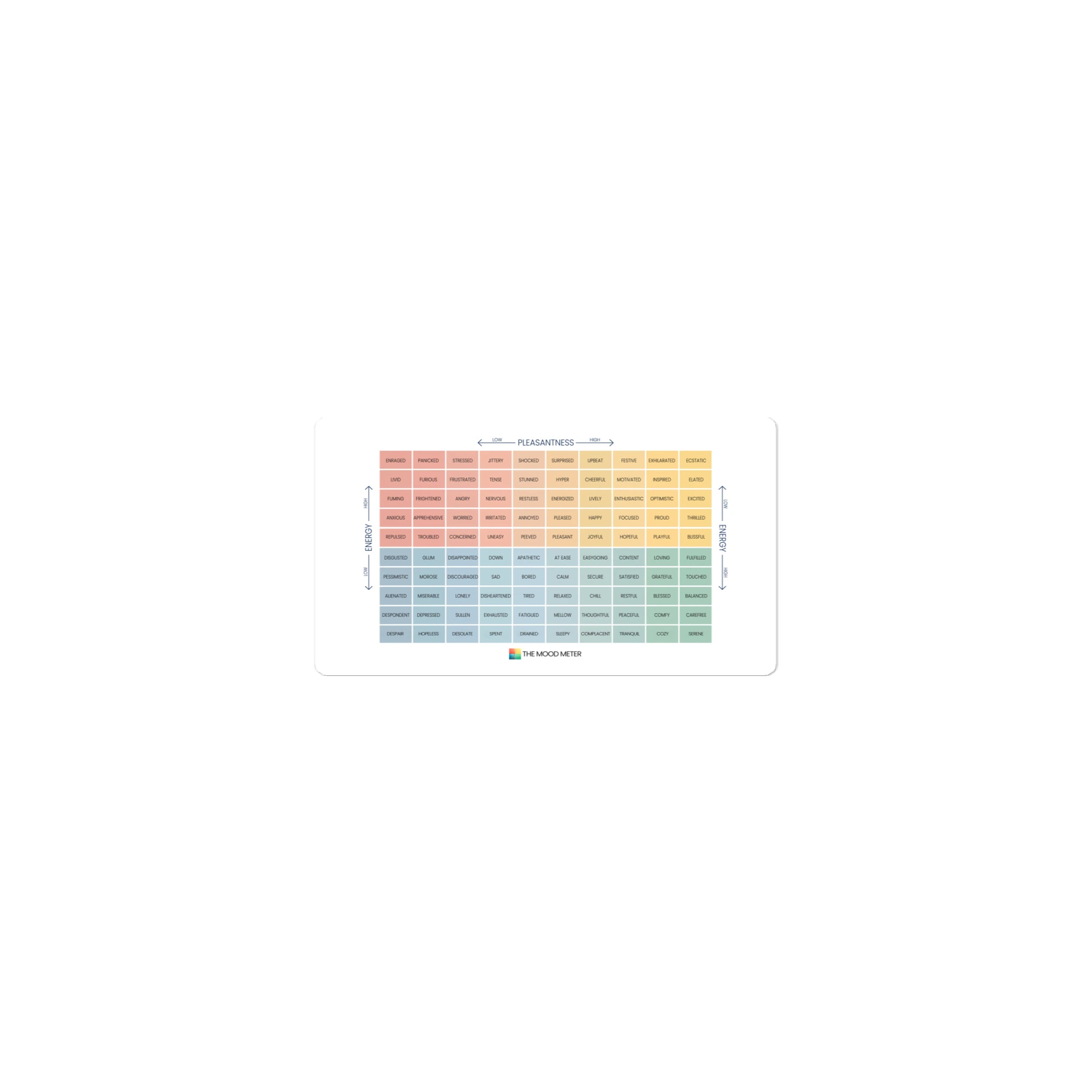
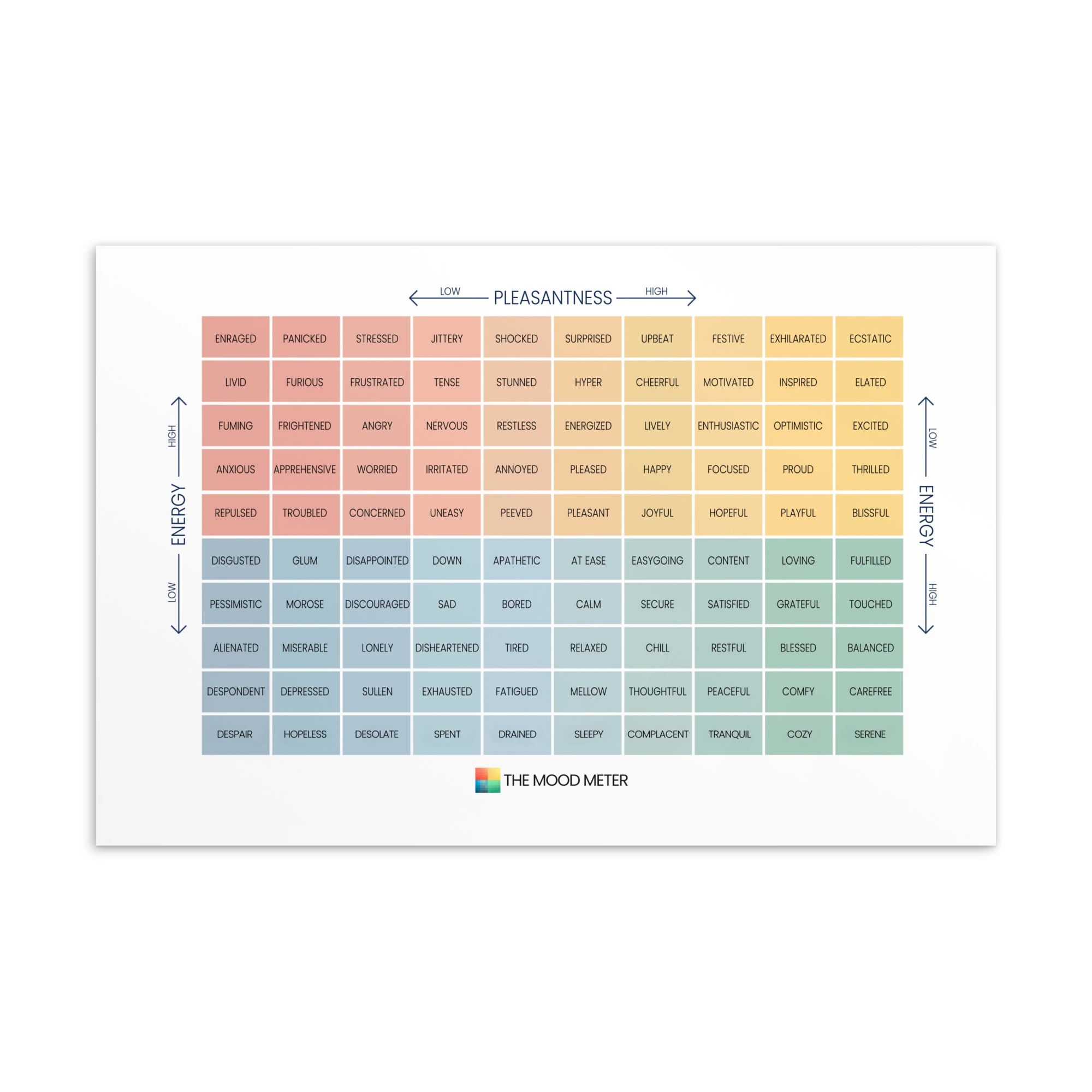
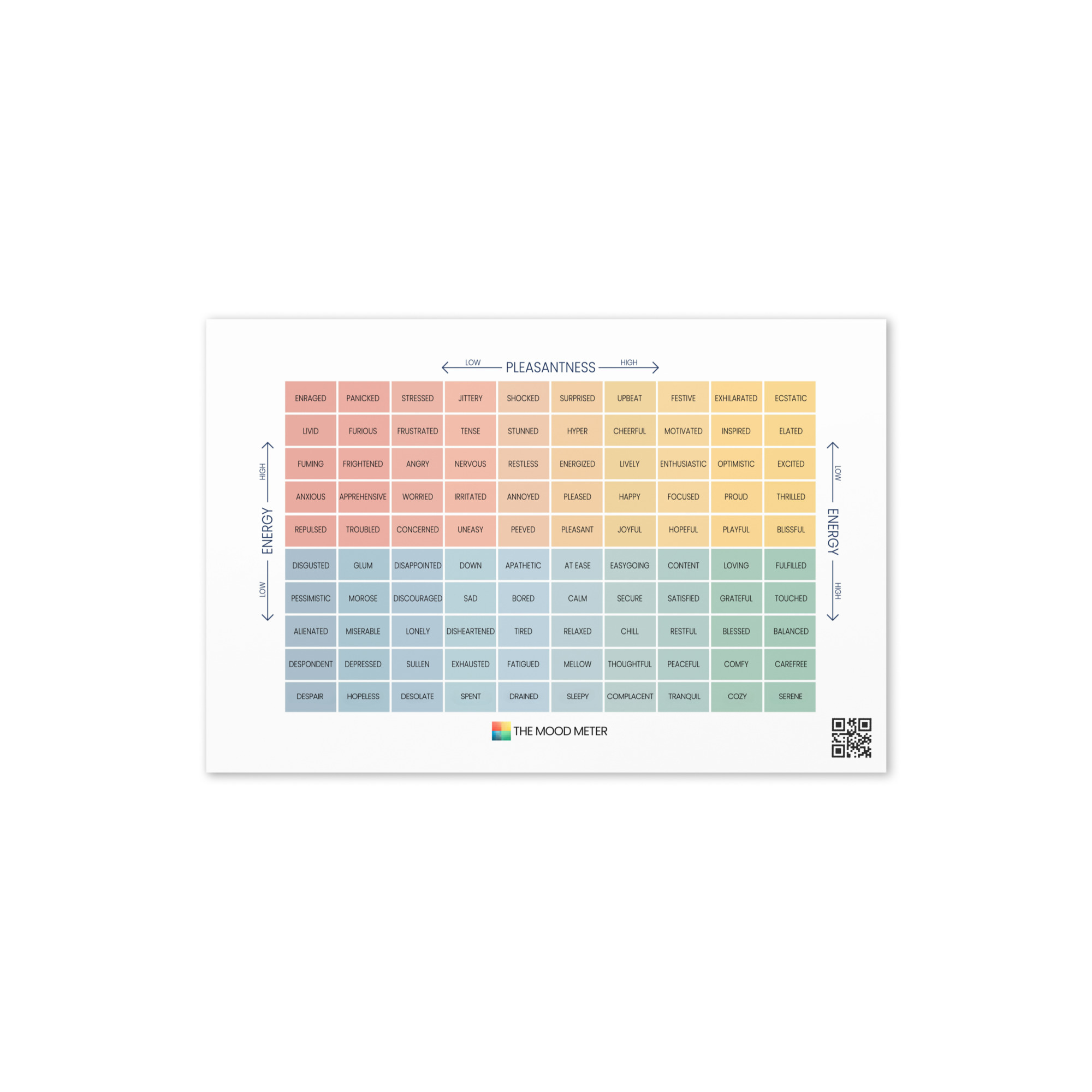
How the Mood Meter Supports Daily EQ Development
An essential tool for applying Goleman’s model is the Mood Meter, a structured emotional-awareness framework developed within the RULER approach. The Mood Meter organizes emotions across four quadrants based on energy and pleasantness, helping individuals identify, label, and understand how emotions shift throughout the day. By using the Mood Meter consistently, we gain clearer emotional vocabulary, improved self-awareness, and stronger regulation techniques. It transforms abstract “feelings” into actionable data that supports better decisions, healthier relationships, and aligned behavior.
Real-World Application: Integrating EQ Into Daily Practice
Emotional intelligence becomes transformative when embedded in daily behavior. We illustrate how individuals can strengthen EQ using structured routines:
-
Morning emotional check-ins: brief labeling of emotions to start the day with clarity.
-
Midday resets: using cognitive or physical grounding techniques to maintain performance.
-
Evening reflection: analyzing emotional triggers and identifying growth opportunities.
-
Communication audits: reviewing how tone, timing, and intent aligned with desired outcomes.
These practices reinforce EQ at a foundational level and create measurable improvements in personal and professional environments.
The Science Behind Emotional Intelligence and Performance
Neuroscience research confirms that EQ impacts the prefrontal cortex (decision-making), amygdala (emotional responses), and anterior cingulate cortex (error monitoring and empathy).
We explain how emotional mastery strengthens neural pathways that support resilience, attention control, and cognitive flexibility. Individuals with high EQ exhibit decreased stress reactivity, enhanced problem-solving capacity, and more reliable behavioral patterns.
EQ in Leadership: The Competitive Advantage
Leaders with strong emotional intelligence outperform their peers because they communicate more effectively, cultivate trust, and inspire teams with purpose.
We outline key benefits such as:
-
Reduced conflict and smoother collaboration
-
Higher employee engagement and retention
-
Better adaptability during organizational change
-
More accurate decision-making under uncertainty
-
Stronger culture and psychological safety
EQ is not a soft skill; it is a strategic leadership asset that directly affects business performance.
EQ for Teams: Building Cohesion and Collective Intelligence
Emotionally intelligent teams demonstrate improved cooperation, creativity, and execution.
We highlight systems that reinforce team-level EQ:
-
Shared emotional vocabulary
-
Transparent communication norms
-
Structured conflict-resolution frameworks
-
Routine mood-awareness check-ins
-
Collaborative reflection cycles
These practices elevate overall team dynamics and accelerate project outcomes.
Mastering the Five Elements of EQ
Goleman’s five elements of emotional intelligence provide a holistic structure for understanding and improving our internal and interpersonal effectiveness.
By strengthening self-awareness, regulating emotions, nurturing motivation, practicing empathy, and enhancing social skills, we create a stronger foundation for leadership, performance, and personal fulfillment. Integrating tools such as the Mood Meter accelerates this growth, making emotional intelligence a measurable and sustainable life skill.