Defining Social and Emotional Learning: Core Skills, Benefits, and the Mood Meter
Defining Social and Emotional Learning: A Complete Guide for Schools and Families
Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) is the structured process through which students and adults develop the skills required to understand emotions, build healthy relationships, make responsible decisions, and create supportive learning communities. When SEL is implemented with fidelity, it strengthens academic outcomes, reduces behavioral disruptions, and enhances overall well-being across schools and districts.
Understanding the Purpose of SEL in Education
SEL offers a research-driven foundation for improving climate, instruction, and student engagement. Schools adopting evidence-based SEL practices benefit from increased attendance, stronger self-management skills, and more positive peer interactions. Educators also gain tools to teach regulation, empathy, and collaborative problem-solving in age-appropriate ways. District-level SEL frameworks typically align with CASEL’s five core competencies: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. To explore these fundamentals in depth, read What Is Social-Emotional Learning? A Complete Guide to SEL in Schools.
The Core Competencies of SEL
SEL development revolves around five interconnected areas, each shaping how students learn and interact in the classroom.
Self-Awareness
Students learn to recognize emotions, strengths, limitations, and personal values. This competency establishes the foundation for confidence, accurate self-perception, and emotional clarity.
Self-Management
Learners develop the ability to regulate emotions, manage stress, sustain motivation, and set achievable goals. Effective self-management directly supports academic persistence and resilience.
Social Awareness
Students build the capacity to empathize with others, understand diverse backgrounds, and interpret social cues. Social awareness improves collaboration and reduces conflict.
Relationship Skills
Learners practice effective communication, teamwork, conflict resolution, and cooperative decision-making. Strong relationship skills contribute to healthier peer and teacher relationships.
Responsible Decision-Making
Students evaluate consequences, consider ethical standards, and make constructive choices. This competency enhances judgment in academic, social, and personal contexts.
How SEL Strengthens Academic Achievement
Research consistently shows that SEL improves academic performance by enhancing focus, reducing classroom stress, and promoting positive behavior. Students with strong SEL skills demonstrate improved problem-solving abilities, higher engagement levels, and lower rates of disciplinary actions. Districts using tiered SEL frameworks report significant gains in both short-term behaviors and long-term graduation outcomes.
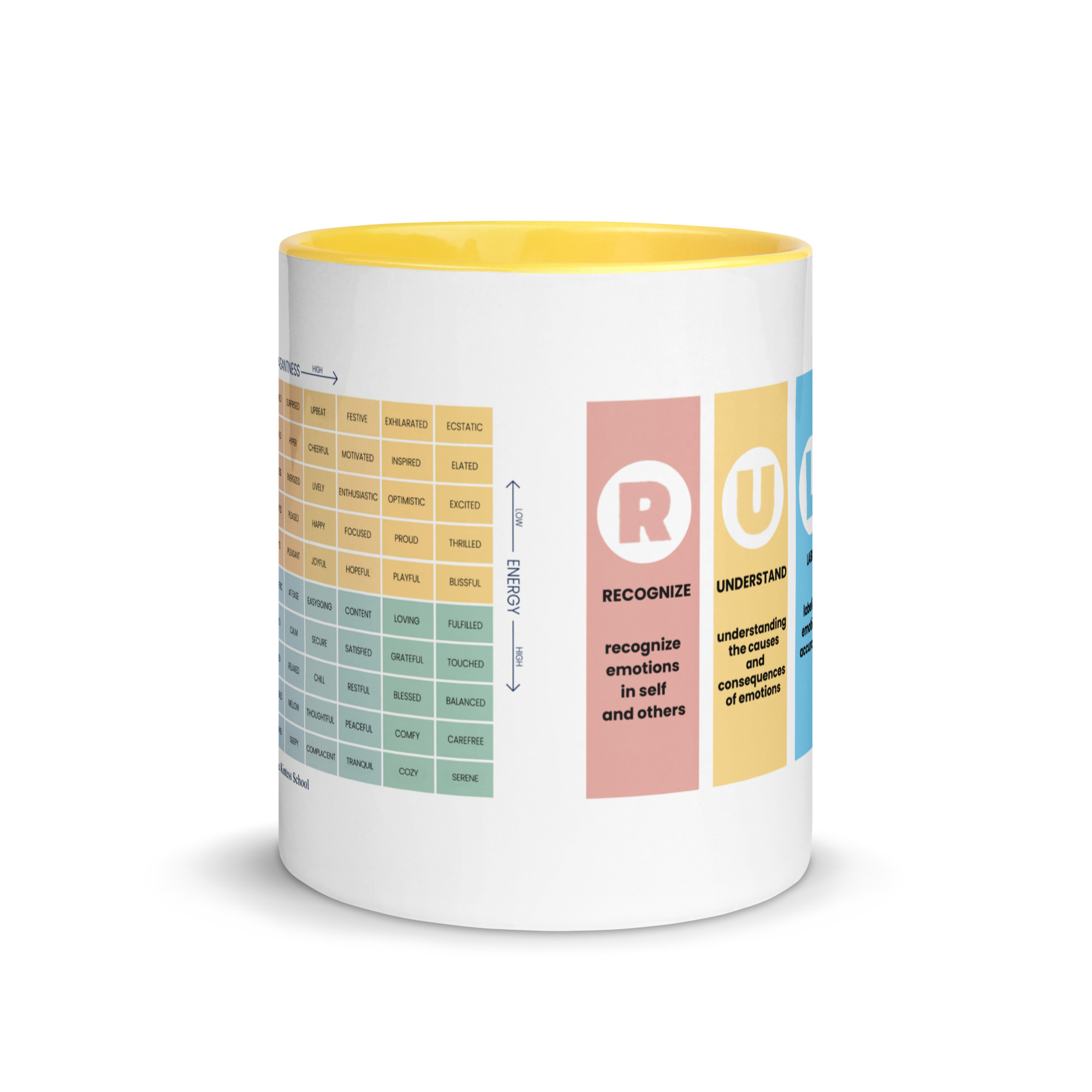
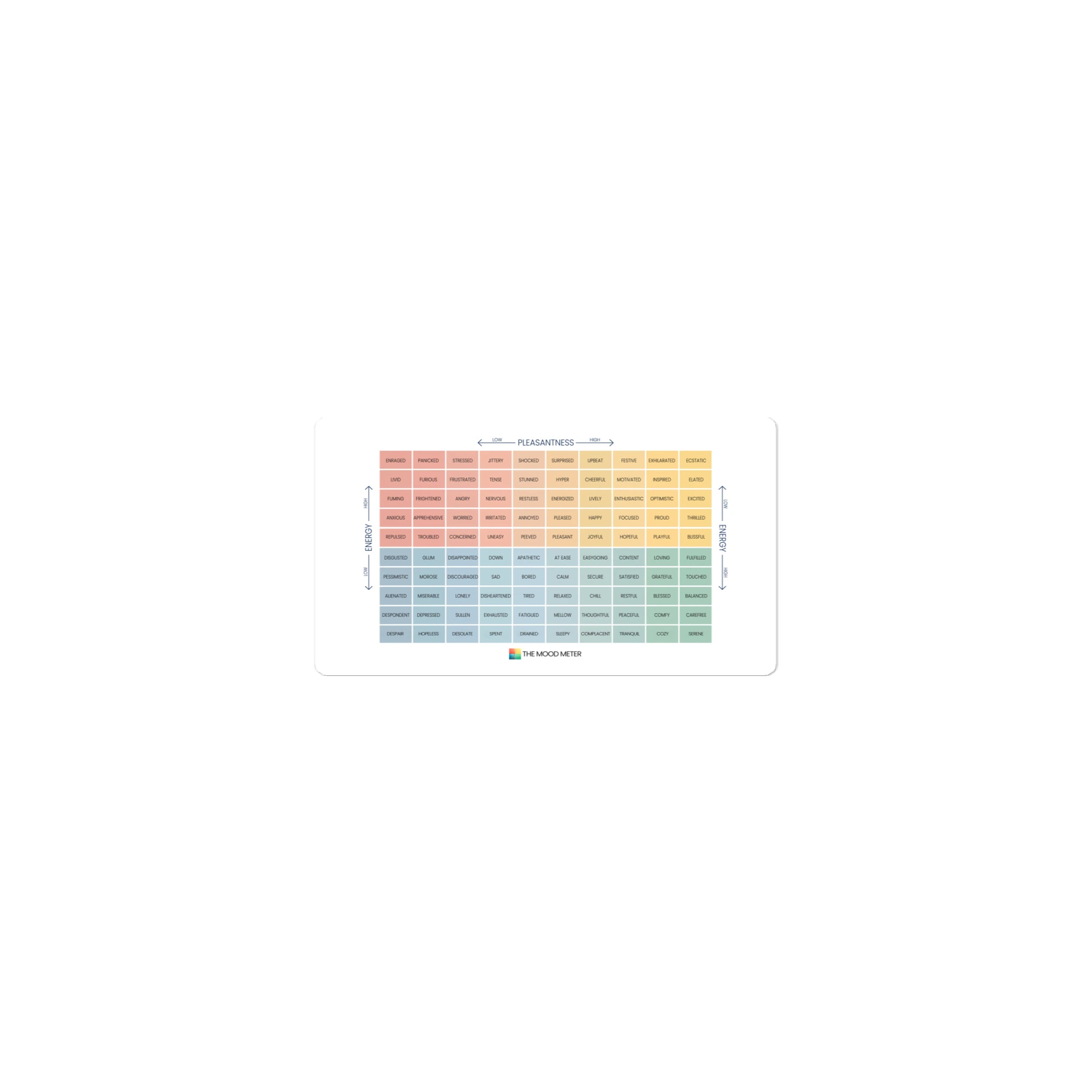
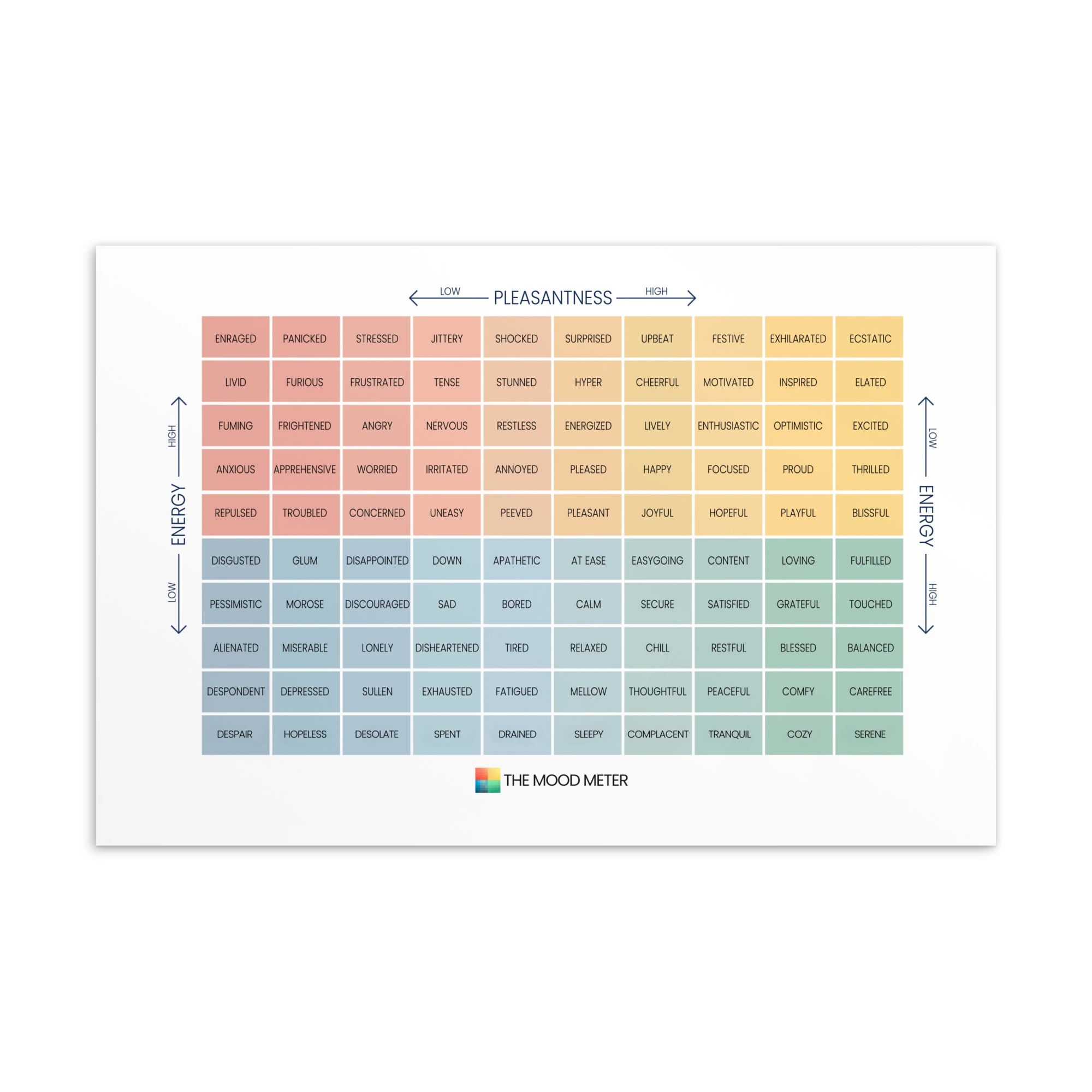
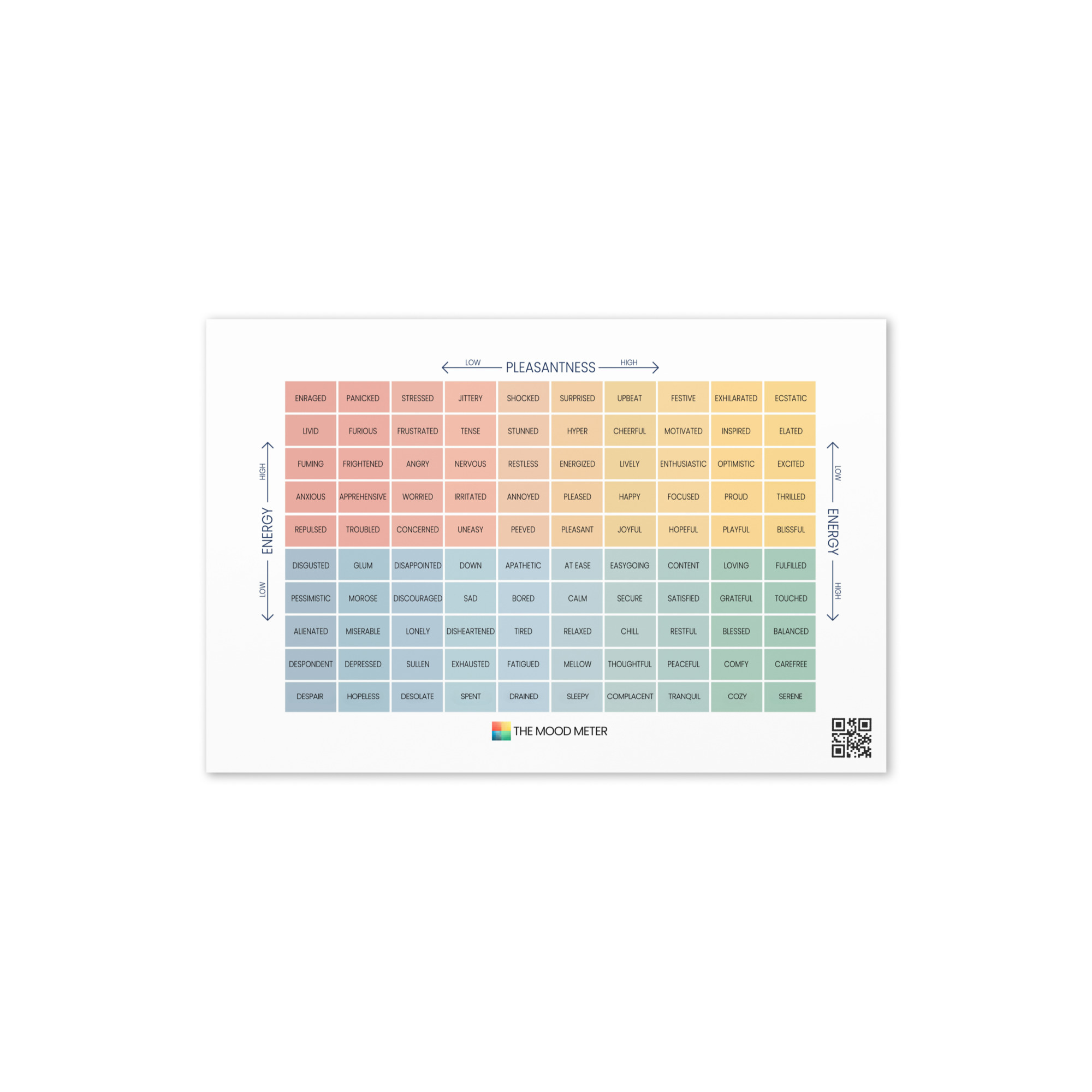
The Mood Meter and Its Role in SEL Development
The Mood Meter is a scientifically designed tool that helps students and educators accurately label and navigate emotions. It maps feelings across four quadrants based on energy and pleasantness, making emotion recognition concrete and accessible. Daily check-ins encourage learners to pause, reflect, and develop emotional vocabulary. Over time, using the Mood Meter strengthens empathy, enhances regulation skills, and promotes healthier responses to stressors in both academic and social settings. To learn more about how the tool works, explore What Is the Mood Meter?.
Implementing SEL Systemically Across Districts
A districtwide SEL strategy works best when it is integrated across policies, classroom practices, leadership training, and family engagement. Effective implementation includes clear learning targets, ongoing professional development, coaching support, and regular progress monitoring. Schools that embed SEL into academics, discipline models, and school culture create consistent expectations that benefit every learner.
SEL for Educators and School Staff
Educators play a central role in modeling and sustaining SEL. Training in emotional regulation, communication strategies, and relationship-building gives teachers stronger classroom management and reduces burnout. Staff with strong SEL skills create climates where students feel safe, supported, and ready to learn. To explore how SEL strengthens teacher well-being and school culture, read SEL for Educators and School Staff: Building Emotional Skills for Stronger Schools.
Family and Community Involvement in SEL
SEL accelerates when families reinforce emotional literacy at home. Parents can support the process by practicing reflection, modeling calm problem-solving, and using shared vocabulary from school SEL programs. Partnerships with community organizations add coherence, cultural relevance, and extended learning opportunities.
Equity-Driven SEL Practices
Authentic SEL must reflect diverse cultural perspectives and promote fair opportunities for all learners. Districts grounded in equity examine how school environments, policies, and instructional practices affect different student groups. Culturally responsive SEL ensures every student feels respected, valued, and empowered.
Measuring SEL Progress and Impact
Schools measure SEL effectiveness using climate surveys, behavioral data, self-assessment tools, and classroom observations. These insights help educators refine instruction, target interventions, and ensure SEL programming remains aligned with district goals.